Sun Valley Solar Doubles Efficiency and Expands Capabilities
"We can now handle 70 to 100 work orders per case manager, thanks to the streamlined process with Field Squared."
- Jim Hutson, Commercial and Residential O&M Manager, Sun Valley Solar.
Transforming Operational Complexity into Service Simplicity

Field Squared was founded in 2014 with a bold vision: to revolutionize field service management through end-to-end business process automation. At the time, field service organizations struggled with disconnected systems, inefficient workflows, and limited real-time visibility. We saw an urgent need for a unified solution—one that would empower businesses to digitally transform their operations from the ground up.
Rather than follow the industry status quo, we built something different—an industry-first innovation that disrupted the field service management space. Unlike traditional software that focuses on a single feature or industry, the Field Squared Field Service Automation Platform was designed to do it all. From automating simple tasks to solving complex operational challenges, our platform delivers a comprehensive, scalable solution that drives efficiency, reduces operating costs, and maximizes productivity.
Unlike generic workforce management tools, Field Squared is designed specifically for the unique demands of mobile field operations. Our platform enables businesses to:
We don’t just create software that looks great and solves operational challenges - we build solutions designed to:
At Field Squared, we are committed to helping field service organizations work smarter, not harder. Our goal is to provide businesses with a powerful, scalable, and easy-to-use platform that transforms how they manage field teams and assets—so they can focus on delivering exceptional service.
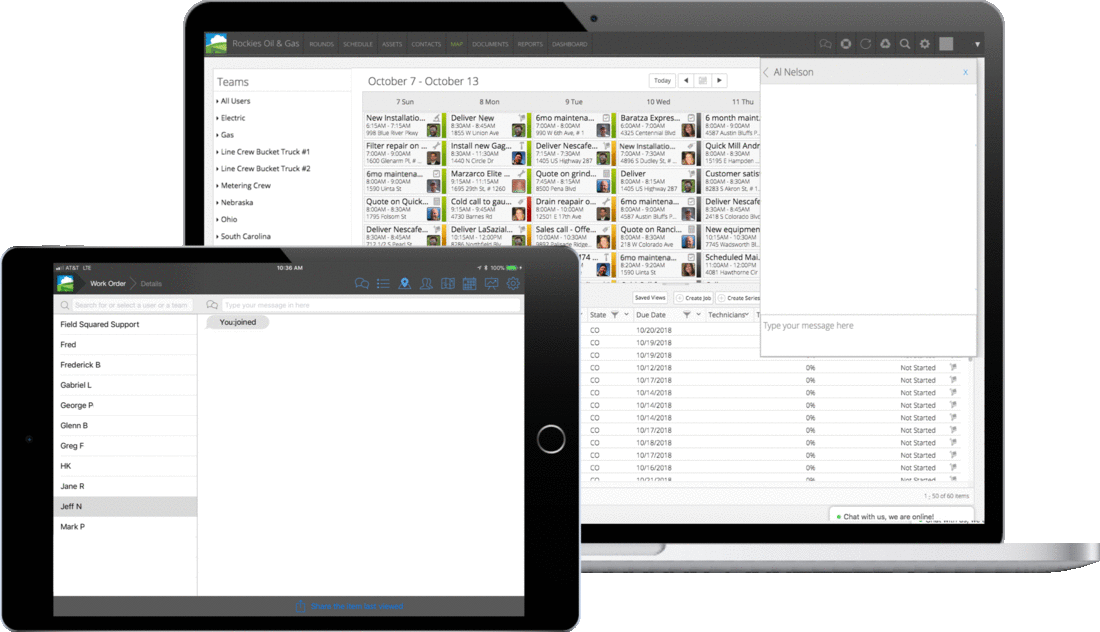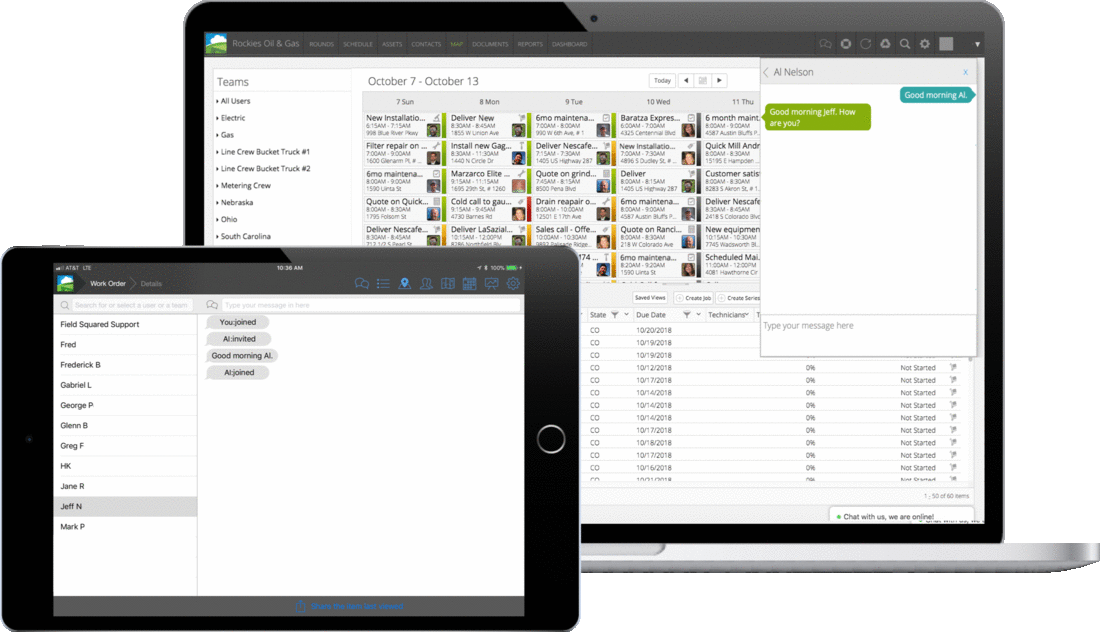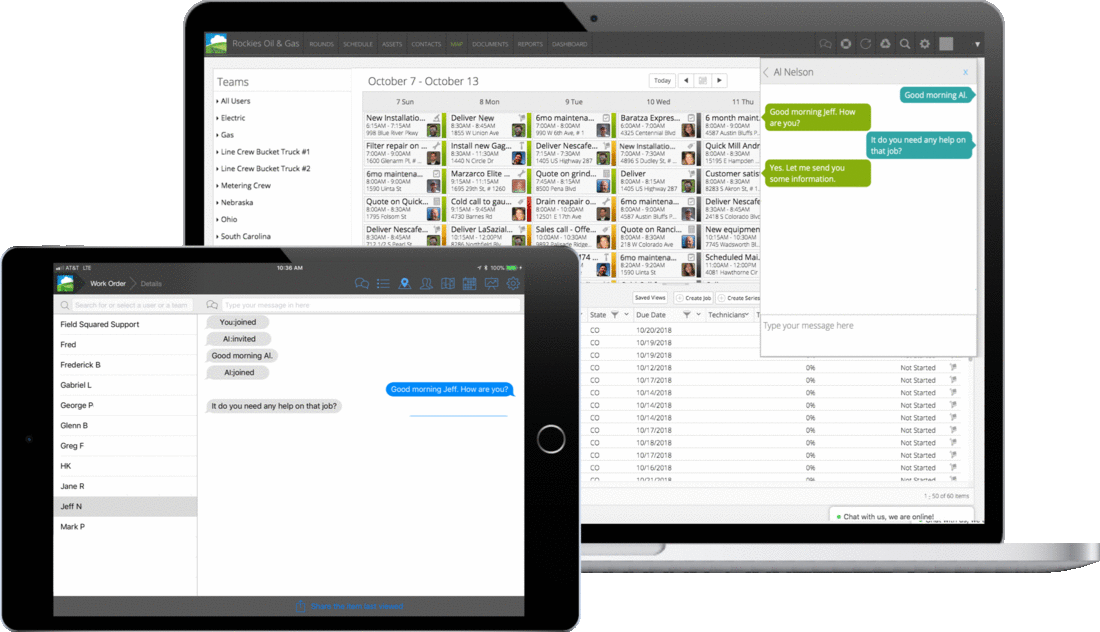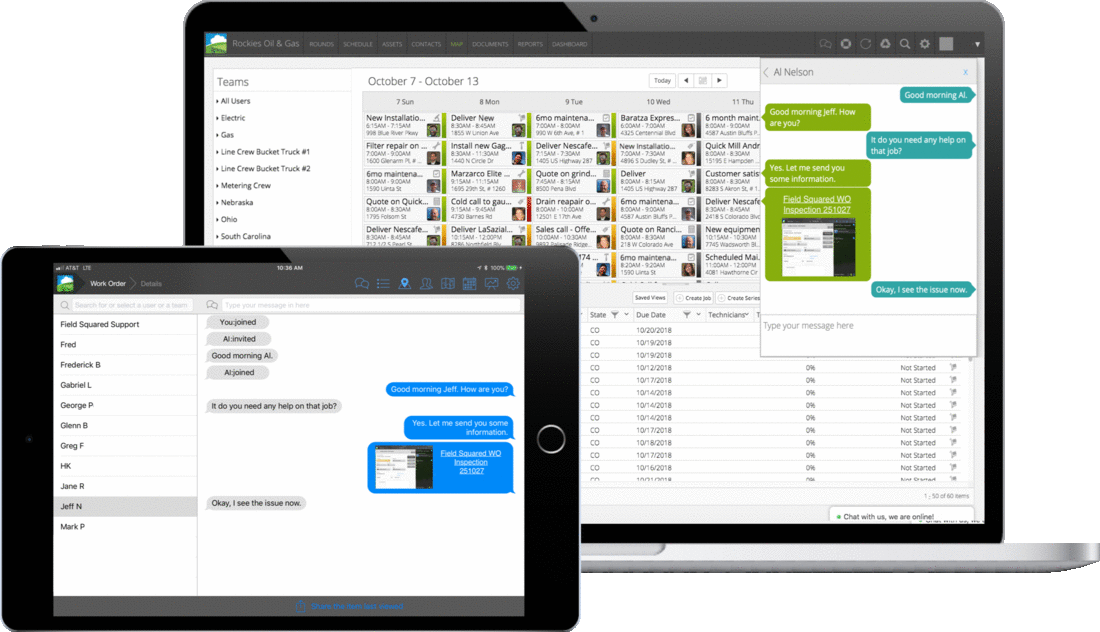
The field service landscape is constantly changing, and so are we. As workforce expectations, AI-driven automation, and predictive analytics become essential to modern field operations, Field Squared continues to evolve to meet the needs of today’s field service leaders including:












Christopher Camut is a seasoned executive and technology innovator with over 25 years of leadership experience transforming how enterprises operate in the field. As CEO of Field Squared, he leads the vision and execution of a cutting-edge mobile workforce management and field service automation platform built for complex industries like telecommunications, utilities, and oil & gas.With a deep understanding of operational efficiency, asset lifecycle management, and digital transformation, Christopher has helped organizations move from paper-based processes to streamlined, data-driven workflows. His leadership has fueled Field Squared’s evolution into a platform that enables companies to drive ROI, boost workforce productivity, and respond to real-time field challenges with precision.Previously, Christopher held executive roles at software and infrastructure companies where he scaled operations and delivered double-digit growth. At Field Squared, he brings together innovation, industry insight, and a relentless focus on solving the most pressing field operations problems.Christopher is a regular contributor to thought leadership around field service trends, AI-driven scheduling, and enterprise asset management. His focus: helping organizations thrive through technology that works where the work gets done.
"We can now handle 70 to 100 work orders per case manager, thanks to the streamlined process with Field Squared."
- Jim Hutson, Commercial and Residential O&M Manager, Sun Valley Solar.
“We've scaled our company up by 300% over seven years, which probably wouldn't have been doable without Field Squared.” - Jim Kent, a Market Vice President Operations, Segra
Read Case Study"We have scaled from doing one to two installs a day to 20 without a single headcount hire."
- Justin Nelson, COO, EVP Engineering and Operations, HyperFiber
"Field Squared has transformed our field operations, allowing us to complete more projects with greater efficiency."
- Sean O'Brien, Market VP of Operations at Oregon Aerial Construction
"Based on our initial rollout, we have already saved an annual amount of $250,000 in overhead costs."
- William Morgan, Implementation Specialist, Great Plains Gas Compression
"Since we've switched to Field Squared, all of our customer responses have been very positive."
- Jim Foley, CFO at Sea Tow
Read MoreAugust 01, 2024
Field Squared is growing. We’re always looking for great talent who is passionate about technology and redefining an entire industry. If you hunger to help field service organizations, love technology, or believe you can change the world, we’d like to talk to you.
Field Squared Headquarters Address:
834 F S. Perry Street, Suite 133
Castle Rock, CO 80104
We’d love to hear from you!
You can email us at info@fieldsquared.com or call us at 1-855-505-2824.
Get in touch with us for a live demo.